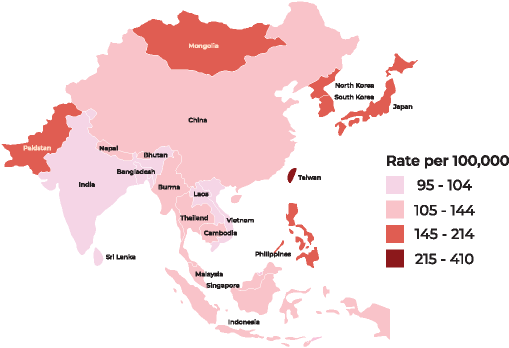
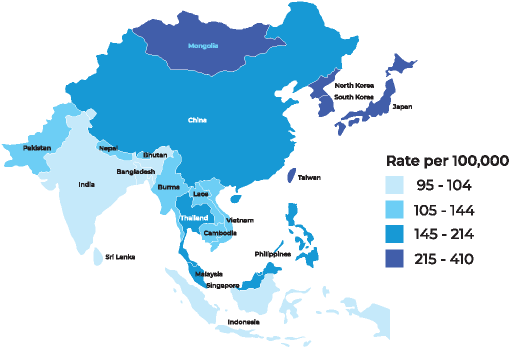
Incidence rates for total cancers in females in Asian Countries
Incidence rates for total cancers in males in Asian Countries
Symptoms of blood cancers may vary individually but commonly can include as follows,
(source: MBCV Report 2018. Image is adopted from MBCV with modification)
Unexplained Weight Loss
Fatigue
Easily Bruised Or Bleed
Feeling Weak or Breathless
Pain in Bones / Joints
Itchy Skin
Enlarged Lymph Nodes
Swollen Stomach or Abdominal Discomfort
Frequent and Repeated Infections
Fever / Night Sweats
Bone Pain (Ribs / Back)
The risk factors for Blood Cancers as follows,
(source: MBCV Report 2018. Image is adopted from MBCV with modification)
Smoking
Chemical Exposures

Chemotherapy Drugs

Radiation Exposure
Certain Blood Disorders
Genetic Defects
The data on blood cancer incidences and survival rate is limited in Asia.
Misconception about Blood Cancer are common:
(source: MBCV Report 2018. Image is adopted from MBCV with modification)
There are many misconceptions about blood cancer, and it is important to learn the facts. Below are some of the common misconceptions about blood cancer.

Diagnosis equated a "death sentence as blood cancer is perceived to be incurable"

Patients and survivors will not be able to regain quality of life.

The causes of blood cancer are not well understood by the public.
For example, some incorrectly think that anemia is a cause of cancer.
Like other cancers, blood cancer is perceived to be contagious
Solid cancers are defined as abnormal cellular growths in “solid” organs such as the breast or prostate, as opposed to leukemia, a cancer affecting the blood, which is liquid.36
Solid tumors may be benign (not cancer), or malignant (cancer). Different types of solid tumors are named for the type of cells that form them. Examples of solid tumors are sarcomas, carcinomas, and lymphomas. (for lymphomas, please refer to blood cancers link for further information). 37

Brain
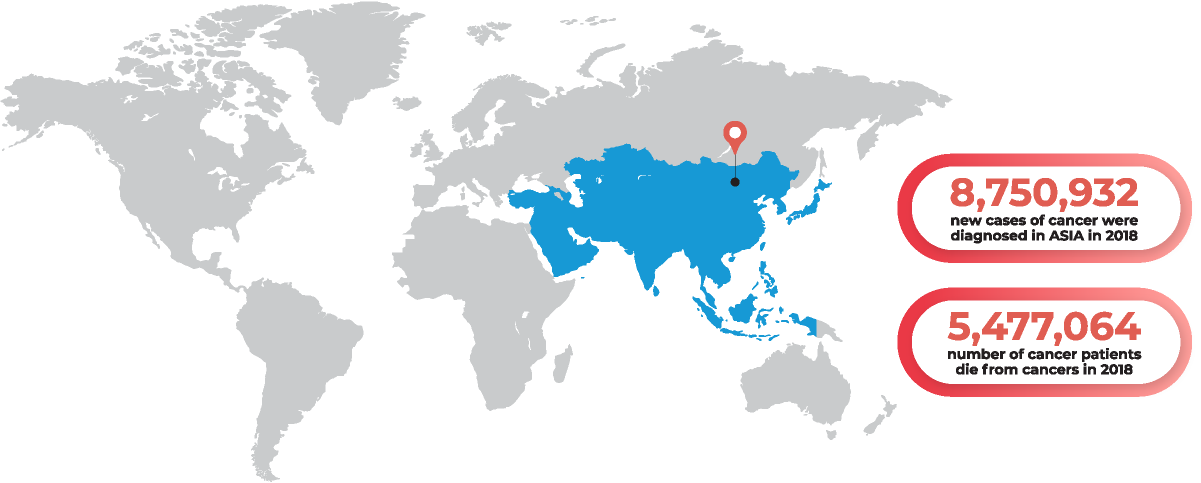
Asia has about half the cancer incidence rate of North America (152.2 cases/100,000 person-years versus 315.6 cases/100,000 person-years). However, the ratio of cancer deaths to the number of new cancer cases in 2012 was much higher in Asia (0.66) than in North America (0.33). 38
Breast
Close to a quarter (24%) of all breast cancers were diagnosed within the Asia-Pacific region (approximately 404,000 cases at a rate of 30 per 100,000), with the greatest number of those occurring in China (46%), Japan (14%) and Indonesia (12%).39

Liver
Liver cancer is a major health problem in developing countries. The highest age adjusted incidence rates (>20 per 100,000) are recorded in East Asia (North and South Korea, China, and Vietnam), and sub-Saharan Africa, which accounts for 82% of liver cancer cases worldwide.40

Colorectum
China, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, Singapore and Turkey had higher 5-year prevalence rates than that in other Asian countries (≥ 46.5/100,000). 41 The temporal trends of these epidemiological figures are different, where China showed an increasing incidence and mortality, Singapore demonstrated rising incidence but reducing mortality, and Japan was reported as having decreasing incidence and mortality. 42
Lungs
Among Asian countries, five countries with the highest standardized incidence rates of lung cancer were Democratic Republic of Korea with 44.2 per 100,000, China with 36.1 per 100,000, Armenia with 35.9 per 100,000, Turkey with 34.7 per 100,000, and Timor-Leste with 31 per 100,000, respectively. 43

Stomach
Many Asian countries, including Korea, Japan and China, experience disproportionately high rates of stomach cancer, possibly due to high rates of Helicobacter pylori infection and the increased consumption of salted and smoked foods. 44

Esophagus
The highest incidence of esophageal cancer in Asian countries was related to Turkmenistan, Mongolia, Tajikistan, Bangladesh, and China. All these countries are a part of the Asian belt of the cancer. Cancer incidence was in the region more than 100 per 100,000. 45

Pancreas
The incidence and mortality of pancreatic cancer varies greatly across regions and populations. In 2012, Eastern and Western Asia (4.5 and 3.9/100,000 ASR) have higher incidence of pancreatic cancers compared to southeast and center of Asia (2.2 and 1.2/100,000 ASR). And the highest rate (6.5/100,000) of ASR incidence is in Australia and New Zealand. 46
Breast, lung, stomach, colorectal and liver cancers constitute the most common cancers in Asia. Prostate cancer is the most common male-specific cancer in Asia and it ranks sixth among all cancers in Asian men, compared to developed countries where prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men. 47
Estimated number of new cancer cases vs. deaths and distribution (%) by type (excludes non-melanoma skin cancer) in Southern, Eastern, and South-Eastern Asia, both sexes, 2018.

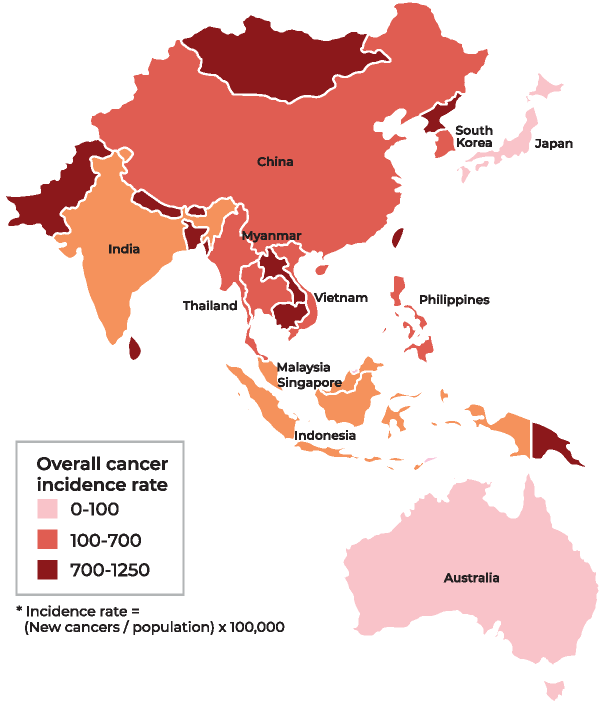
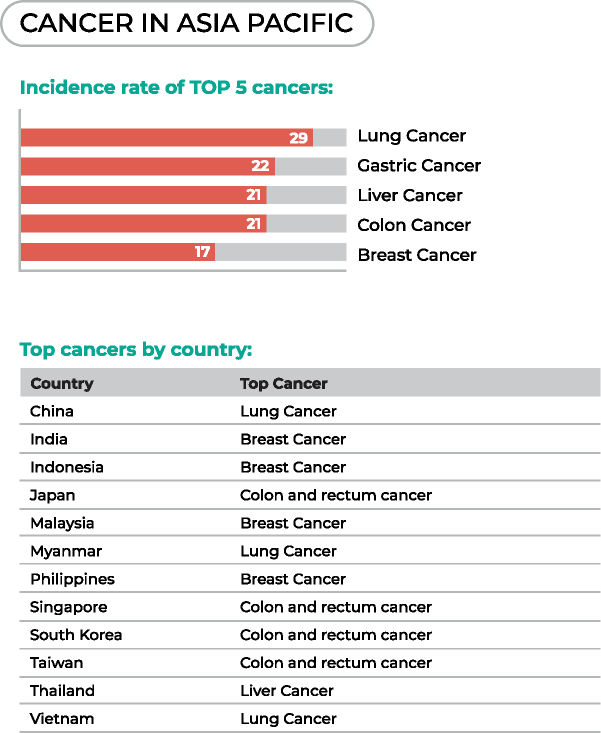
Cancer is the second-leading causes of death in Asia, accounting for 15 of every 100 deaths, according to Global Health Data Exchange, 2016. The top five cancers in the region are lung cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, colon cancer and breast cancer. But for women, breast cancer is the most common.